-
Surveying Reflector Prism
-
Survey Mini Prism
-
360 Degree Prism
-
Total Station Prism
-
Prism Pole Bipod
-
Carbon Fibre Telescopic Pole
-
Telescopic Levelling Staff
-
Tribrach Adaptor
-
Instrument Tripods
-
Total Station Batteries
-
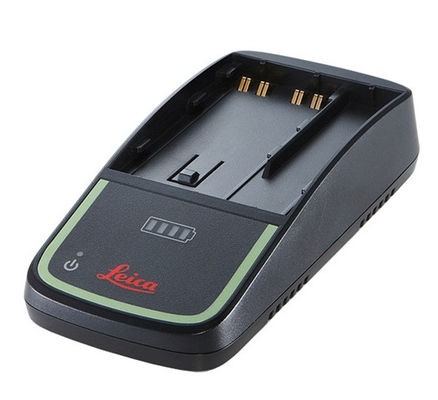
Total Station Battery Charger
-
Total Station Cable
-
Total Station Accessories
-
Surveying Instrument
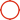
GKL311 12v Li Ion Battery Charger GEB242 520g Single Bay Total Station
| Model | GKL311 | Color | Black |
|---|---|---|---|
| Batteries | GEB211 GEB212 GEB221 GEB222 GEB241 GEB242 GEB371 Battery | Input | 12-24V/2A |
| Output | 12-24V/2A | Weight | 520g |
| Port | DC | Protection | Over-charging, Overcurrent, Overvoltage |
| Used For | Total Station | Type | Electric |
| Warranty | 1 Year | Certificate | CE |
| Highlight | GKL311 12v Li Ion battery charger,520g 12v Li Ion battery charger,GEB242 |
||
Leica GKL311 Professional 3000 Single-Bay Total Station Battery Charger for GEB211 GEB212 GEB221 GEB222 GEB241 GEB242 GEB371 Battery
Model: GKL311
Specifications:
| Model | GKL311 |
| Color | Black |
| Batteries | GEB211 GEB212 GEB221 GEB222 GEB241 GEB242 GEB371 Battery |
| Input | 12-24V/2A |
| Output | 12-24V/2A |
| Weight | 520g |
| Port | DC |
| Protection | Over-charging, Overcurrent, Overvoltage |
| Used For | Total Station |
| Type | Electric |
| Charging Time | 8 Hours |
| Certificate | CE |
Features:
1. The Leica GKL311 Professional 3000 Single-Bay battery charger charges a li-lon battery within 8 hours.
2. It has an onboard LED light that shows the progress of the charge.
3. This Leica charger works with many Leica brand batteries.
4. Providing high quality power, long life, reliable quality and long working hours.
5. With PTC protection device, that prevents overcharge, discharge, overcurrent (short circuit) and overheating.
What is the best charger for Leica batteries?
Highend charger, optimally designed for batteries used by Leica Geosystems. Intelligent battery recognition and controlled charging for longest battery service life. Charging and discharging cycles to refresh old cells.
How long will the battery last?
There are two factors: runtime and charge-discharge cycles.
Runtime is a measure of how much time can elapse before a fully charged battery reaches a charge of 0%. Technically a battery never reaches a 0% charge but a low charge does not permit enough power to be transmitted to the device.
Runtime is controlled by capacity and usage. Capacity is measured in Amp hours or milliamp hours. Battery capacity quantifies the total amount of energy stored within a battery. More capacity equals longer runtime between battery charges. Hence if you want a battery to last the longest possible be sure to buy a battery with the highest possible capacity. For example a battery it a capacity of 2000 mAh will last longer in between charges than a battery with 1500 mAh capacity.
Runtime is also increased or decreased by usage.
All batteries slowly drain regardless if you are using it in your device or not! Once charged an electron flow occurs in a battery and once begun the electron flow will continue until the chemical is exhausted.
Chemical depletion occurs with every charge-discharge cycle. What is actually occurring during this charge-discharge cycle is replenishing spent electrons (i.e. creating current – an electrical flow)). In batteries electricity is created by charging two chemicals in a solution. This is done by applying an electrical flow (i.e. from a wall or car charger or solar charger) to the battery’s lithium.
Charging lithium can be thought of as the introduction of ions or movement of chemistry. To move the lithium chemistry (lithium-ion, lithium polymer, lithium iron phosphate, etc) you have to have a minimum voltage applied to the lithium. Most battery cells are charged to 4.2 volts with relative safe workings at about 3.8 volts. Anything less than 3.3 volts will not be enough to charge or move the chemistry. One thing to note here is that volts are an algorithmic measurement of current. So in a sense to create current through your battery you have to introduce current into your battery’s lithium .
Introducing current into your lithium is called intercalation. Intercalation is the joining of a molecule (or molecule group) between two other molecules (or groups). When it comes to charging your battery you are in effect pushing ions in and out of solid lithium compounds. These compounds have minuscule spaces between the crystallized planes for small ions, such as lithium, to insert themselves from a force of current. In effect ionizing the lithium loads the crystal planes to the point where they are forced into a current flow. The current flow is then channeled back and forth from anode to cathode and thereby creating an electrical flow to power on your device. Again this can done 300-500 times before all the ions are pushed out of the lithium and you will no longer be able to charge your device.
The number of charge-discharge cycles that can be done to a battery ranges between 300 and 1000 times depending on the chemical of the battery. In addition after each charge-discharge cycle the runtime (time between charges) is reduced by intercalation as discussed above. For example you may notice in the first 3-4 months you are getting between 3-5 hours of runtime on your battery. Then in months 5-12 (after your purchase) you notice that you are slowly getting less and less runtime in between charges until you might be getting less than 5 minutes of runtime. This is the normal use of the chemistry inside your battery and DOES NOT mean that the battery is bad, but simply the chemical has been spent.
![]()