-
Surveying Reflector Prism
-
Survey Mini Prism
-
360 Degree Prism
-
Total Station Prism
-
Prism Pole Bipod
-
Carbon Fibre Telescopic Pole
-
Telescopic Levelling Staff
-
Tribrach Adaptor
-
Instrument Tripods
-
Total Station Batteries
-
Total Station Battery Charger
-
Total Station Cable
-
Total Station Accessories
-
Surveying Instrument
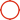
6600mAh Ashtech GPS Battery ProMark 5/206402 for GPS Ashtech Promark100, Promark 200, ProMark 5

Contact me for free samples and coupons.
WhatsApp:0086 18588475571
Wechat: 0086 18588475571
Skype: sales10@aixton.com
If you have any concern, we provide 24-hour online help.
x| Voltage | 3.6V | Capacity | 6600mAh |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type | Li-lon | Weight | 200g |
| Color | Black | Temperature | 10~40 °C |
| Rechargeable | Yes | Condition | New |
Ashtech GPS Battery ProMark 5/206402 for GPS Ashtech Promark100, Promark 200, ProMark 5
Model: PM5/206402
Specifications:
| Voltage | 3.6V |
| Weight | 200g |
| Type | Li-ion |
| Capacity | 6600mAh |
| Package | Individual Box Package |
| Warranty | 12 Months |
| Temperature | 10~40°C |
| Rechargeable | Yes |
| Used For | TOPCON GPS Ashtech Promark100, Promark 200, ProMark 5 |
Features:
1. Our batteries are manufactured with top quality cells using the most up-to-date technology to ensure a long lasting charge with no memory effect.
2. Our batteries are brand new, they are not original and they are 100% OEM compatible.
3. Works and charges the same as the original battery.
4. All of our batteries are featured with stable circuit protection, over charging protection, over heat protection and short circuit protection.
5. Comes with 12 months manufacturer warranty.
6. Safety, CE, RoHS approval.
What will cause my battery to lose power?
A battery over time degrades and eventually stops working. In fact the battery from its very first charge begins a very slow process that causes the battery to cease from functioning. Collectively the process is called battery degradation and power loss and it includes the following: declining capacity, increasing internal resistance, elevated self-discharge, and premature voltage cut-off on discharge.
Declining capacity is when the amount of charge a battery can hold gradually decreases due to usage, aging, and with some chemistry, lack of maintenance.
The loss of charge acceptance of the Li ion/polymer batteries is due to cell oxidation. Cell oxidation is when the cells of the battery lose their electrons. This is a normal process of the battery charge creation process. The capacity loss is permanent because the metals used in the cells run for a specific time only and are being consumed during their service life.
Internal resistance, known as impedance, determines the performance and runtime of a battery. It is a measure of opposition to a sinusoidal electric current. A high internal resistance curtails the flow of energy from the battery to a device. The aging of the battery cells contributes, primarily, to the increase in resistance as does cell oxidation. Interestingly energy may still be present in the battery, but it can no longer be delivered due to poor conductivity.
Elevated Self-discharge: All batteries have an inherent self-discharge. The self-discharge on nickel-based batteries is 10 to 15 percent of its capacity in the first 24 hours after charge, followed by 10 to 15 percent every month thereafter. Li-ion batteries self-discharge about five percent in the first 24 hours and one to two percent thereafter in the following months of use. At higher temperatures, the self-discharge on all battery chemistries increases. The self-discharge of a battery increases with age and usage. Once a battery exhibits high self-discharge, little can be done to reverse the effect. Be sure never to leave a rechargeable battery at low charge for long periods, even during storage.
Premature Voltage Cut-Off: Some devices do not fully utilize the low-end voltage spectrum of a battery. A device may cut itself off before the designated end-of-discharge voltage is reached leaving battery power in the battery unused. For example, a pda that is powered with a single-cell Li ion battery and is designed to cut-off at 3.7V may actually cut-off at 3.3V. Obviously the full potential of the battery and the device is lost (not utilized). Why? It could be something with elevated internal resistance and or operations at warm ambient temperatures. Devices that load the battery with current bursts are more receptive to premature voltage cut-off than analog equipment. High cut-off voltage is mostly equipment related, not battery.
![]()
![]()
![]()