-
Surveying Reflector Prism
-
Survey Mini Prism
-
360 Degree Prism
-
Total Station Prism
-
Prism Pole Bipod
-
Carbon Fibre Telescopic Pole
-
Telescopic Levelling Staff
-
Tribrach Adaptor
-
Instrument Tripods
-
Total Station Batteries
-
Total Station Battery Charger
-
Total Station Cable
-
Total Station Accessories
-
Surveying Instrument
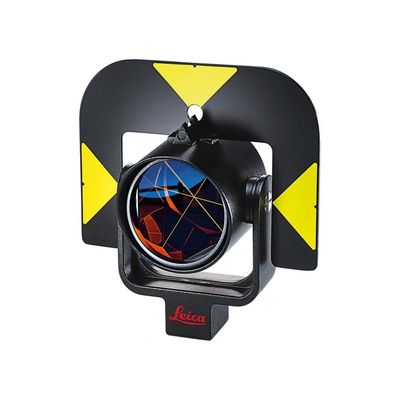
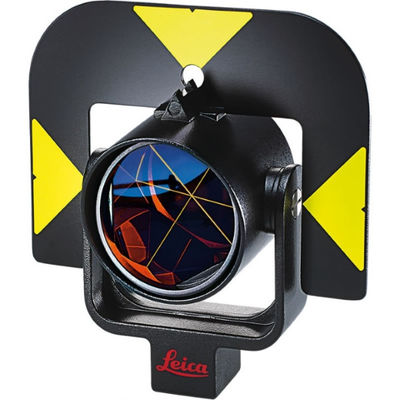
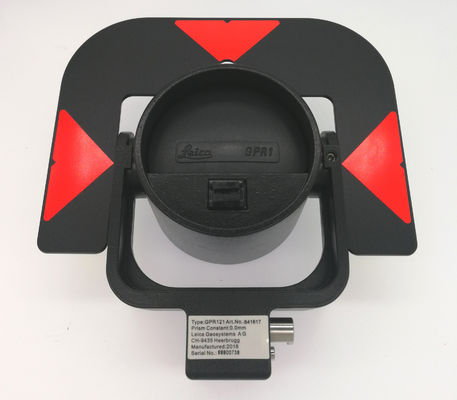
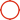
GPR121 Surveying Reflector Prism 3500m Circular Prism Holder
| Holder | Metal | Constant | 0mm |
|---|---|---|---|
| Range | 3500m | Centering Accuracy | 1.0mm |
| Color | Black | Brand | Leica |
| Target Plate | Removable | Prism Type | Circular |
| Highlight | 3500m Circular Surveying Reflector Prism,GPR121 Surveying Reflector Prism,3500m Circular prism holder |
||
Leica Precision Circular Surveying Reflector Prism with Holder GPR121
Model: GPR121
Specifications
| Prism Constant | Range | Centering Accuracy |
| 0mm | 3500m | 1.0mm |
Features
Removable Target Plate
Metal Holder
100% Original Leica brand Prism
Precision circular prism with anti-reflection coating, mounted in metal holder.
Optical Survey Prism Applications
Surveying reflector prisms are used by surveyors and engineers to measure the change in position of a target that is assumed to be moving. Survey prisms are used for a wide range of monitoring applications including:
· Rail Monitoring
· Settlement Monitoring
· Displacement Monitoring
· Deformation Monitoring
· Convergence Monitoring
Prism Range
Surveying Prisms, also known as retro-reflectors, redirect a measuring beam back to the EDM (Electronic Distance Measurement) for processing distance. There are two main factors for good range measurement: prism diameter and beam deviation. If the beam deviation is not accurate then the returned beam will miss the EDM completely. This occurs mainly near the maximum range of the EDM.
Prism Holder Accuracy
Prism accuracy is determined by the physical location of the prism in its canister and then to the prism holder.
Survey Prism Offsets
Some Surveying Prisms have an offset due to the fact that the transmitted beam from the EDM takes longer to enter and exit the prism. The longer time translates to a longer distance measured. The distance is corrected by using an 'offset' and/or positioning the prism in relationship to the plumb line of the prism holder. Common offsets are 0, -17.5 mm, -30 mm, -34 mm, and -40 mm. The offset is determined by multiplying the height of the prism against the refractive index of the glass used.
![]()